Receipt


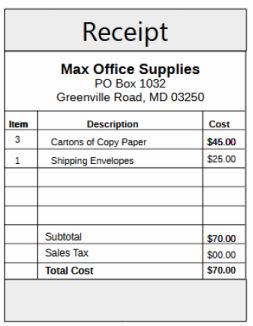
In this tutorial I will show you how to record the sales tax you pay to the government in GnuCash.

Deciding what type of business to start involves considering several factors, including your interests, skills, market demand, and the resources available to you. Here are some steps to help you determine the best business for you:
Here are a few examples of popular Online and Offline business ideas to consider:
Choosing the right business type requires thoughtful consideration and planning. Reflect on your passions, skills, market opportunities, and resources to find the best fit for you.
For individuals with a felony record, finding suitable jobs can be challenging, but there are industries and types of work that are more open to second-chance hiring. Here are some of the best job types and industries where men and women with felony convictions may find opportunities:
Many trades focus more on skills and training than on background checks. Pursuing vocational training or certifications can improve chances in these fields:
Some transportation jobs, especially if they do not require customer interaction, may offer opportunities:
Starting a small business can bypass many of the traditional hiring hurdles:
Restaurants and other service-related industries often hire individuals with a criminal record:
For those who have a knack for technology or are willing to learn:
If traditional employment is a challenge, self-employment or gig work might be a more accessible path:
Some nonprofits and faith-based organizations hire those with felonies and focus on rehabilitation:
Jobs in fields like painting, roofing, general labor, and demolition are often available for people with a felony.
Remote work is a growing field and can offer flexibility:
Organizations that promote second-chance hiring, such as Goodwill Industries or Homeboy Industries, may also offer job placement services.
Additionally, federal bonding programs and tax credits for employers who hire felons can make some businesses more inclined to offer opportunities.

Organizing a backpack drive for underprivileged children is a wonderful and impactful initiative. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
By following these steps, you can effectively coordinate a backpack drive that makes a significant difference in the lives of underprivileged children in your community.

The profitability of products on Etsy can vary based on trends, consumer preferences, and the uniqueness of your offerings. Keep in mind that success on Etsy often depends on finding a niche or creating unique, high-quality products. Here are some general categories and types of products that have been popular on Etsy:
Planners
Planners are popular and profitable, the popularity and profitability of planners can depend on current trends, target demographics, and unique features. Certain types of planners have been popular on Etsy and in the market in general. Keep in mind that trends can change, so it’s essential to stay updated.
Here are some popular and potentially profitable types of planners:
When creating planners for sale, consider the quality of materials, the layout’s user-friendliness, and any unique features that set your planners apart from others on the market. Additionally, pay attention to customer reviews and feedback to continuously improve your products. Keep in mind that staying abreast of current trends and incorporating them into your designs can contribute to the profitability of your planner products.
Financial planners are most popular
Financial planners come in various types, and their popularity often depends on the needs and preferences of the users. The popularity of a financial planner can also be influenced by trends in personal finance and productivity. Here are some types of financial planners that have been popular:
Keep in mind that trends in personal finance and planning may evolve, and new types of financial planners may gain popularity. It’s crucial to stay informed about current financial management practices and incorporate relevant features into your financial planner products. Additionally, user-friendly interfaces, clear goal-setting capabilities, and customization options can contribute to the popularity of financial planners.
Before deciding on a product, it’s essential to research and stay updated on current trends. Additionally, consider your own skills, interests, and resources to create a product that you can passionately market. Keep an eye on Etsy’s own resources and guides for sellers, as they provide valuable insights into what works best on the platform. Remember that customer service, high-quality photos, and effective SEO optimization are crucial for success on Etsy.

LibreOffice is a powerful and free office suite, used by millions of people around the world. Its clean interface and feature-rich tools help you unleash your creativity and enhance your productivity. LibreOffice is compatible with a wide range of document formats such as Microsoft® Word (.doc, .docx), Excel (.xls, .xlsx), PowerPoint (.ppt, .pptx), and Publisher. You can open your Microsoft document in LibreOffice.
But LibreOffice goes much further with its native support for a modern and open standard, the Open Document Format (ODF). With LibreOffice, you have maximum control over your data and content – and you can export your work in many different formats including PDF. LibreOffice includes several applications that make it the most versatile Free and Open Source office suite on the market:
The writer has all the features you need from a modern, full-featured word processing and desktop publishing tool. It’s simple enough for a quick memo, but powerful enough to create complete books with contents, diagrams, indexes, and more. You’re free to concentrate on your message, while the Writer makes it look great.
Calc is the free spreadsheet program you’ve always needed. Newcomers find it intuitive and easy to learn, while professional data miners and number crunchers appreciate the comprehensive range of advanced functions. Built-in wizards guide you through choosing and using a comprehensive range of advanced features. Or you can download templates from the LibreOffice template repository, for ready-made spreadsheet solutions.
In Impress, creating and editing slides is very versatile thanks to different editing and view modes: Normal (for general editing), Outline (for organizing and outlining your text content), Notes (for viewing and editing the notes attached to a slide), Handout (for producing paper-based material), and Slide Sorter (for a thumbnail sheet view that lets you quickly locate and order your slides).
Draw lets you produce anything from a quick sketch to a complex plan, and gives you the means to communicate with graphics and diagrams. With a maximum page size of 300cm by 300cm, Draw is an excellent package for producing technical drawings, brochures, posters, and many other documents. Draw lets you manipulate graphical objects, group them, crop them, use objects in 3D, and much more.
The base is a full-featured desktop database front end, designed to meet the needs of a broad array of users. Base caters to power users and enterprise requirements, providing native-support drivers for some of the most widely employed multi-user database engines: MySQL/MariaDB, Adabas D, MS Access, and PostgreSQL. In addition, the built-in support for JDBC- and ODBC-standard drivers allows you to connect to virtually any other existing database engine as well.
Math is LibreOffice’s formula editor and can be invoked in your text documents, spreadsheets, presentations, and drawings, enabling you to insert perfectly formatted mathematical and scientific formulas. Your formulas can include a wide range of elements, from fractions, terms with exponents and indices, integrals, and mathematical functions, to inequalities, systems of equations, and matrices.
You can start Math either as a stand-alone application directly from the LibreOffice Start Center or directly from within other LibreOffice applications such as Writer, Calc, Impress and Draw.
LibreOffice includes the ability to create and embed charts. Their style, color, and size can be customized in a broad variety of ways – pie charts, square and round columns, trend graphs, dots, 2D and 3D charts, and so much more.